MRO Taxonomy
The adoption of an MRO taxonomy classifying inventory items and indirect materials, enables you to analyze inventory consumption through a single lens while taking better control of your MRO material procurement and inventory. An effective MRO taxonomy also helps maintenance, procurement, and operations teams to manage materials based on their attributes and specifications, rather than just based on an SKU number.
Applying a unified MRO taxonomy to the supply chain ecosystem is a necessary first step to analyze MRO spend, reduce costs, drive operational efficiencies, improve supplier terms, and lower inventory costs. Enventure has the expertise and a deep understanding of industry-standard taxonomy such as UNSPSC, eCl@ss, ECCMA/ eOTD, and many others such schema commonly used for indirect materials. Enventure has also developed its own proprietary MRO taxonomy, based on our experience in Master Data Management, serving clients from various industries over the last two decades. Our MRO taxonomy is very diverse, covering more than 10,000 commodities and suitable for any asset-intensive industry, such as in mining, food, and beverages, pharmaceuticals, oil and gas, utilities, etc. The Enventure taxonomy has a multi-level classification (Nouns, Modifiers, Sub-modifiers) and has an associated dictionary, which covers all key attributes, abbreviations, value definitions and Units of Measure(UoM).
We also provide customized taxonomies for clients who may have specific needs or expectations; a custom schema takes into account a variety of factors, such as the materials in use, supply base, application/usage of the taxonomy, ERP or EAM system and needs of various stakeholders who use the data.
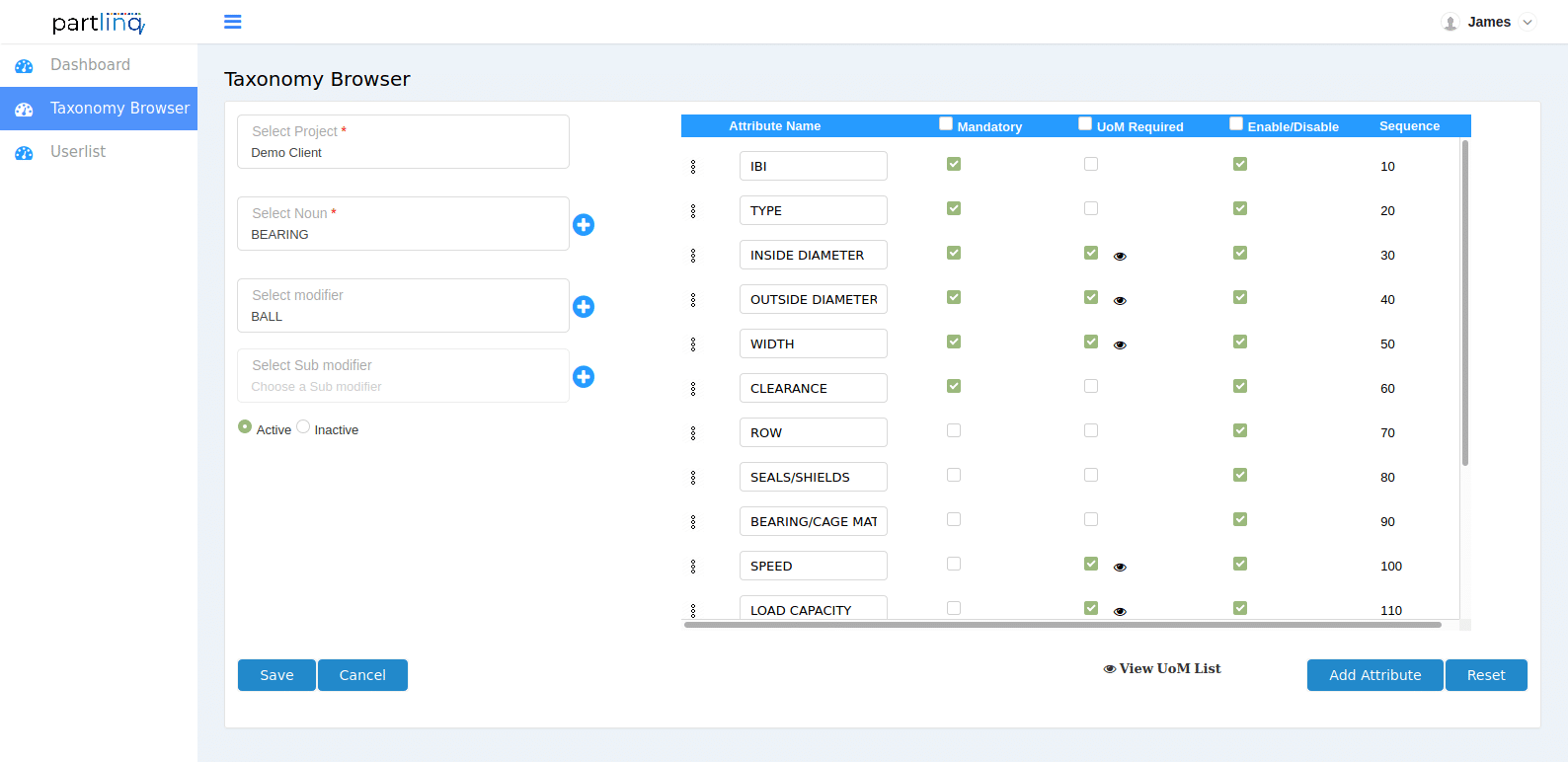
Sample of MRO Data Taxonomy:
- Noun – A broad grouping for a set of products. Examples of Nouns are belt, fastener, pump, bearing, etc.
- Modifier – A sub-classification for each Noun, based on the type of product, application or other similar criteria that helps uniquely identify a subgroup. As an example, for the Noun “BELT”, the modifiers would be TOOTHED, V, CONVEYOR, etc.
- Sub-modifier: A Modifier may in some cases cover a broad variety of items, in which case a sub-modifier would be useful. As an example of a Sub-modifier is:
- Attributes – Specific characteristics of a product, that serve as specifications for the item. Examples of Attributes for a V BELT would be TYPE, BELTY NUMBER, TOP WIDTH, THICKNESS, INSIDE CIRCUMFERENCE, OUTSIDE CIRCUMFERENCE, etc.
- Sub-modifier: A Modifier may in some cases cover a broad variety of items, in which case a sub-modifier would be useful. As an example of a Sub-modifier is:
- Modifier – A sub-classification for each Noun, based on the type of product, application or other similar criteria that helps uniquely identify a subgroup. As an example, for the Noun “BELT”, the modifiers would be TOOTHED, V, CONVEYOR, etc.
For each attribute, the data dictionary also defines what attributes are mandatory, how it can be abbreviated for creating short descriptions, and the Units of Measure (UoM), where applicable.
The major benefits from implementing an effective MRO taxonomy are not just limited to improving data quality; a good taxonomy provides deep visibility to spend patterns, improves maintenance plans, reduces MRO inventory overstock, reduces procurement costs and enhances plant reliability.