The most effective supply chain risk management strategy!
Supply chain risk management (SCRM) is a process for identifying, assessing, and then mitigating the risks involved in the supply chain.
Suppliers like vendors, service providers, contractors, and systems integrators contribute vital input to each organization. Suppliers, on the opposite hand, can provide an advert risk. The business discipline of supply chain risk management (SCRM) strives to grasp and minimize supplier risk.
Life cycle of SCRM
- Risk Identification – The only way to deal with risk is to prevent it from occurring in the first place. The risk management lifecycle begins with the creation of a risk profile, which is subsequently updated through active monitoring.
- Risk Assessment – Recognize the possible effect of a risk event on your business. Keep a watch out for partners that can significantly affect your sales, margins, or profit.
- Risk Mitigation – There is a need to define both preventive and reactive action plans. These are the foundations to address risk and implement necessary measures to ensure supply and trademark protection.
- Supply Chain Risks in the supply chain can be classified as “known” or “unknown.”
The “Known risks” include:
- critical equipment failure within a single-source supplier,
- unpredictable weather disrupting delivery schedules,
- unpredictable price increase of critical raw materials,
- receipt of defective components,
- labor shortages, government tax increases, legislative changes, and so on.
The “Unknown risks” has two components:
- The first stage is to map out the supply chain using a process flow diagram, choose process steps,
- The second is to calculate the impact of losing that step in the process flow without understanding what caused the risk.
Where does managing supply chain risk starts?
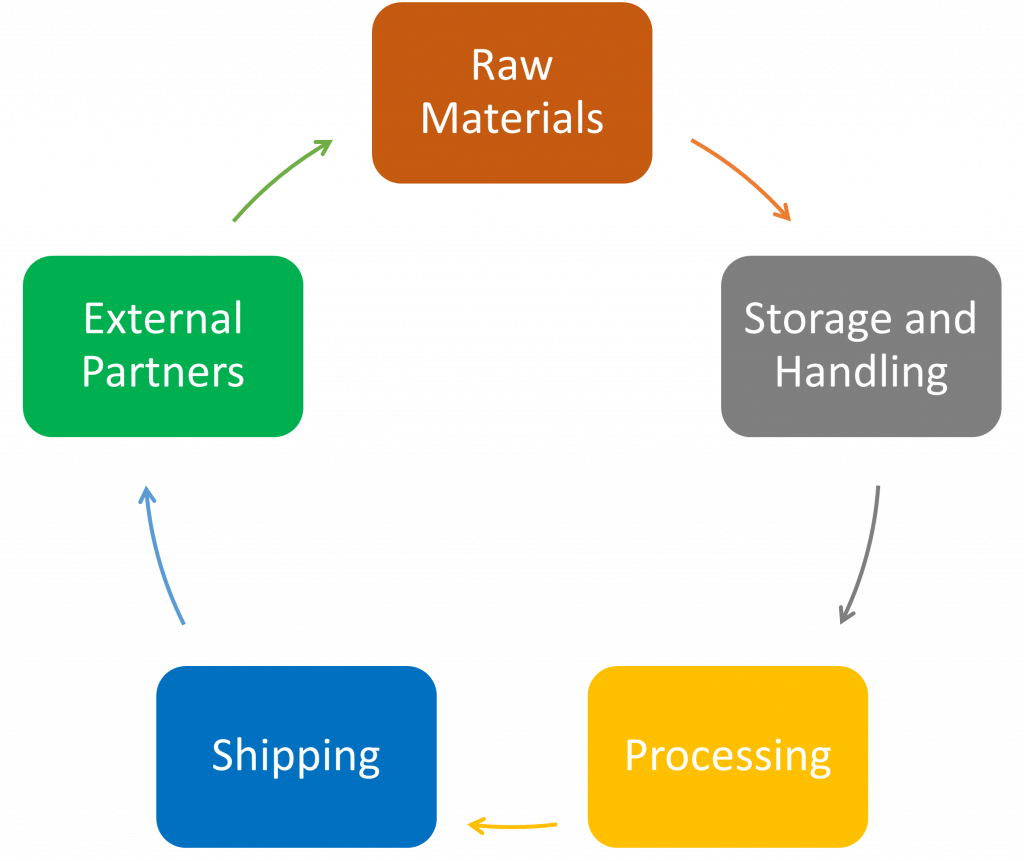
- Raw Materials: Raw materials such as raw materials, ingredients, packaging materials, chemicals, or other components utilized to make your products, can present many risks to a facility.
- Storage and Handling: Several risks in storage and handling include allergy management, temperature control, foreign material control, correct segregation, and product flow.
- Processing: The presence of Proper sanitation, cross-contamination/contact potential, foreign material contamination, critical control point deviations, pre-requisite program failures, and mislabeling are some of these issues.
- Shipping and Transport: Finally, after the product has left your plant, you must secure your shipping and transportation protocols to account for any potential danger. Temperature management, truck and storage unit condition and cleanliness, loading/unloading methods, security/tampering possibilities, accident/emergency recovery, and traceability are all factors to consider during your risk assessment.
Benefits of SCRM
An effective Supply Chain Risk Management promotes supply chain flexibility and responsiveness. The more adaptable a supply base, the faster it can respond to changing demand, and hence the smaller the inherent risks.
- The practice of detecting vulnerabilities along a supply chain encourages open communication flows. Thus, resulting in improved knowledge of supply chain difficulties, which may result in better partnerships.
- Sub-suppliers, for example, with inadequate equipment maintenance regimens pose a danger to the integrity of the whole supply chain. As a result, there is a heavy emphasis on developing rules across the supply chain, with advantages flowing to all parties involved.
Do you want to learn how to mitigate supply chain risks? Talk to one of our Supply Chain specialists today!










